reading-notes
Code Fellows courses Notes
This project is maintained by QamarAlkhatib
TDD with Python
TDD is a methodology in software development that focuses on an iterative development cycle. The emphasis is placed on writing test cases before the actual feature or function is written. This process helps ensure correctness of the code – but also indirectly evolve the design and architecture of the project.
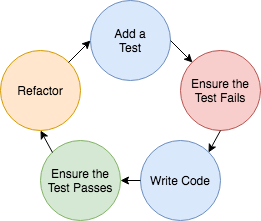
TDD usually follows the Red-Green-Refactor” cycle:
- Add a test to the test suite
- (Red) Run all the tests to ensure the new test fails
- (Green) Write just enough code to get that single test to pass
- Run all tests
- (Refactor) Improve the initial code while keeping the tests green
-
Repeat
If name equals main
If the interpreter is running a main program that has the module name as its main variable, it sets the special title variable to have a value of main.
Every Python module has its own name, which indicates that the module is being run as a standalone program. If the script is imported, the name of the module is set to the script/name.
Example:
# Python program to execute
# main directly
print ("Always executed")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print ("Executed when invoked directly")
else:
print ("Executed when imported")
What is Recursion?
recursive function is a process that occurs when a function calls itself recursively. It can be commonly used to solve various problems.
Example:
# Program to print factorial of a number
# recursively.
# Recursive function
def recursive_factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return n
else:
return n * recursive_factorial(n-1)
# user input
num = 6
# check if the input is valid or not
if num < 0:
print("Invalid input ! Please enter a positive number.")
elif num == 0:
print("Factorial of number 0 is 1")
else:
print("Factorial of number", num, "=", recursive_factorial(num))